基本技

剣術の基本
Kenjutsu (剣術) - Sword Techniques
This page will serve you as a reminder to practice the basics of kenjutsu (剣術). The kata presented below are adapted from an old school (koryu, 古流) called Kashima Shin-ryu (鹿島神流).
The place of weapons in Aikido
Many of O Sensei's students have added a patchwork of weapon techniques in a more or less codified way to their own empty-handed teaching, and today we see many teachers introducing elements of iaido, jodo, and even other classical schools in their teaching. Although not essential, weapons practice can be very beneficial for progression, but the body mechanics governing different weapon systems vary widely. The main thing is therefore less which weapon system one uses than whether the mechanics that govern the movements are in phase with the way in which one moves with bare hands.
Note that the emphasis on the sword is quite representative of the educational nature of budo since in reality, the sword was primarily a symbol of rank and has historically been used relatively little on the battlefield. In this sense, the weapons of the samurai (武器, buki) should be seen as mere utensils (器, ki). If accomplished, a warrior may well use any other utensil than a sword or spear, or even a pair of chopsticks. The way he uses his body will dictate how he wields the buki, not the other way around.
Reishiki (礼式, Etiquette)
Some people "use" budo, as in the sense of buki, where ki means "tool". They "use" thsi tool to become stronger, or to move up in the hierarchy in order to eventually "use" others.
However, being in a budo is the opposite, you have to "serve" others. The word samurai comes from "serving" (侍う), serving one's art, serving one's master, serving one's peers, one's elders but also one's juniors (in Japan, having one or more kohai is a very demanding responsibility).
Budo is a path, not a tool, and etiquette reminds us of that at all times.
Kamae (構, Guards)
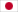
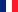
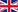
Mu gamae (無構え, no guard): This is the most used guard. It can be translated as "guard without guard". It leaves the body completely open, free to respond to all attacks. Drop your hands and direct the tip of the sowrd to the right, in thesame line as that of the right foot, which is slightly opened to the right.
Hasso kamae (八相構え, eight phases/aspects guard): Hold the sword with the tip of the blade pointed upwards on the right side with the hands at shoulder height. Keep your elbows close to your body.
Waki kamae (脇構え,side guard/ready position): Bring your right foot behind with a fairly large gap between the feet. The sword is positioned on the right with the tip facing down and back. The sharp side of the blade is facing up. Keep your hands clsoe to your hips, towards the back. If placed correctly, the oppenent will have minimal visibility on your blade.
Basic Strikes
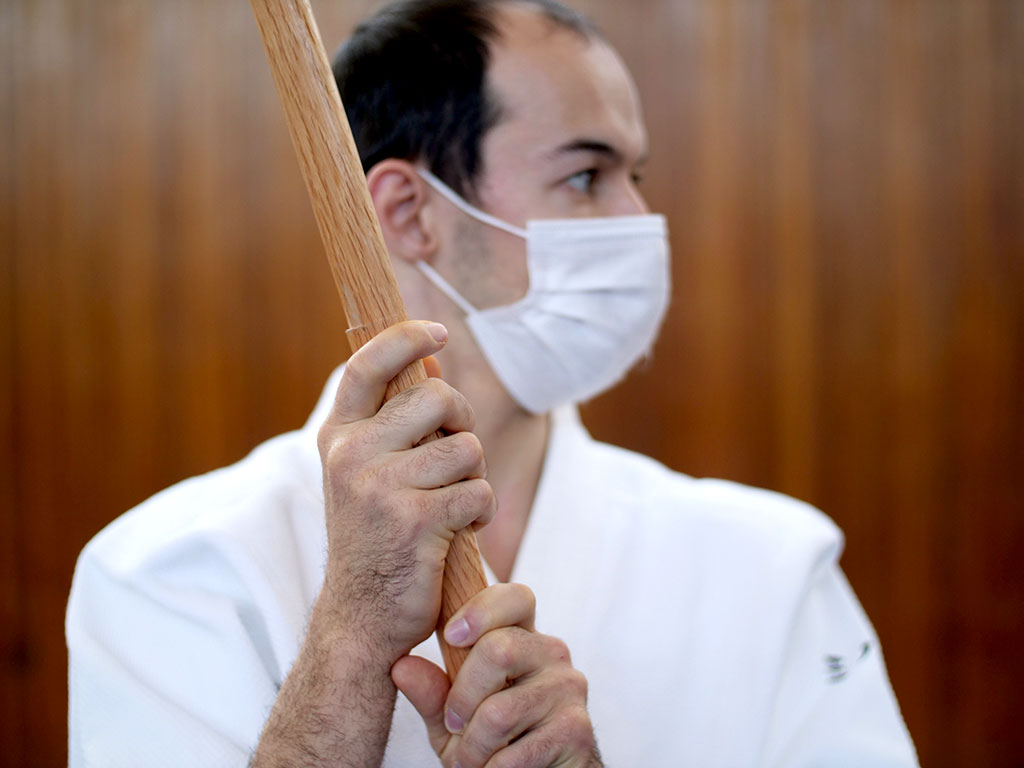
Hold the weapon by grabbing from above, not from the side. Some wood should not be visible between the two hands when gripping a weapon and taking the so-called seigan guard. I personally leave about a fist length between the two hands.
During strikes, it is the palm of the hand that stops the sword, not the thumb. And most importantly, when the sword is not in front of you, but in a mobile position, it is imperative to keep the fingers together and especially the palm of the hand in permanent contact with the hilt. Always keep your thumb in line with your forearm.
Shomen uchi (正面打ち, Strike to the front)
When you put the force in the little finger, you should rest your body weight on external part of the feet. Conversely, when you strike and the force goes through the index finger, you shoudl switch to the internal supports of the feet.
In short, when you apply the grip of the force (as you raise), you should stand of the par tof the foot used for reception. When you use the grip of precision (as you strike), you should use the part of the foot for propulsion.
Kiri kaeshi (切り返し, Cutting repeatedly)
As you raise your hands up, losen your grip to let the sword fall naturally on your side and to your back. Resume tighter control as you ready to strike down.